The breakthrough enhances scientific understanding of the dangerous storms and their long-term impacts on the climate.
Reno, Nev. (September 29, 2025) – On September 5, 2020, California’s Creek Fire grew so severe that it began producing it’s own weather system. The fire’s extreme heat produced an explosive thunderhead that spewed lightning strikes and further fanned the roaring flames, making containment elusive and endangering the lives of firefighters on the ground. These wildfire-born storms have become a growing part of fire seasons across the West, with lasting impacts on air quality, weather, and climate. Until now, scientists have struggled to replicate them in Earth system models, hindering our ability to predict their occurrence and understand their impacts on the global climate. Now, a new study provides a breakthrough by developing a novel wildfire-Earth system modeling framework.
The research, published September 25th in Geophysical Research Letters, represents the first successful simulation of these wildfire-induced storms, known as pyrocumulonimbus clouds, within an Earth system model. Led by DRI scientist Ziming Ke, the study successfully reproduced the observed timing, height, and strength of the Creek Fire’s thunderhead – one of the largest known pyrocumulonimbus clouds seen in the U.S., according to NASA. The model also replicated multiple thunderstorms produced by the 2021 Dixie Fire, which occurred under very different conditions. Accounting for the way that cloud development is aided by moisture lofted into the higher reaches of the atmosphere by terrain and winds is key to their findings.
“This work is a first-of-its-kind breakthrough in Earth system modeling,” Ke said. “It not only demonstrates how extreme wildfire events can be studied within Earth system models, but also establishes DRI’s growing capability in Earth system model development — a core strength that positions the institute to lead future advances in wildfire–climate science.”
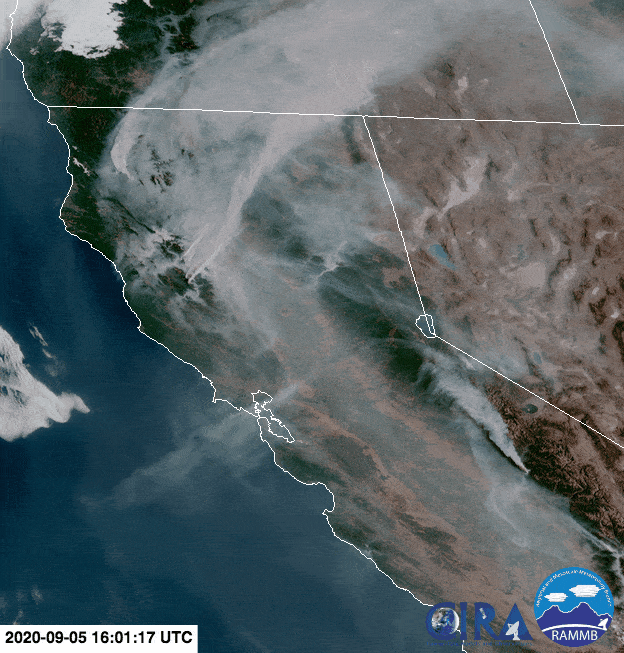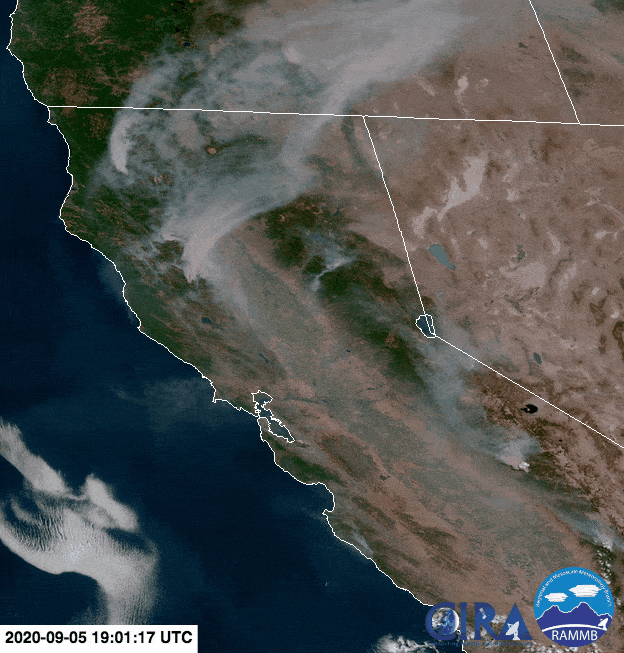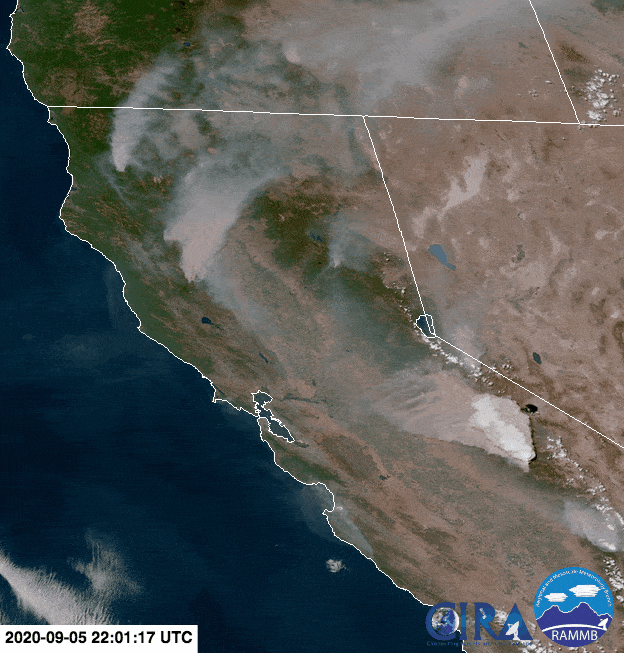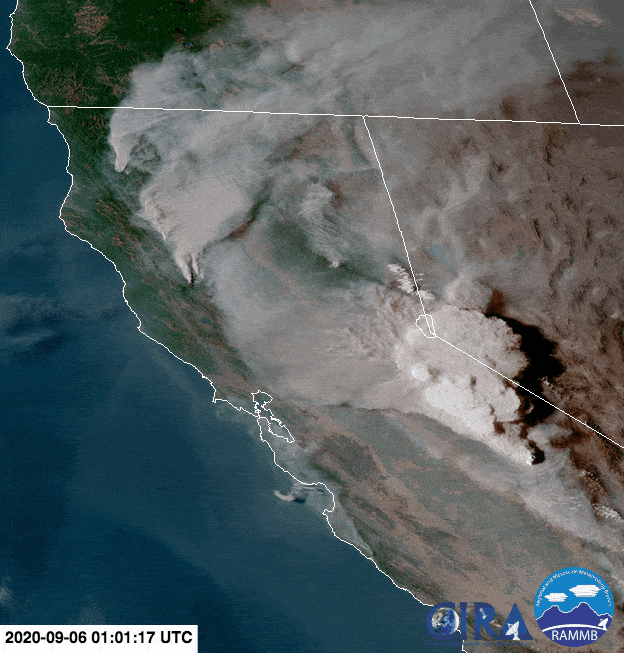
Animation of the formation of a pyrocumulonimbus above the 2020 Creek Fire in California (seen near the lower right edge of the screen). Credit: NOAA
When a pyrocumulonimbus cloud forms, it injects smoke and moisture into the upper atmosphere at magnitudes comparable to those of small volcanic eruptions, impacting the way Earth’s atmosphere receives and reflects sunlight. These fire aerosols can persist for months or longer, altering stratospheric composition. When transported to polar regions, they affect Antarctic ozone dynamics, modify clouds and albedo, and accelerate ice and snow melt, reshaping polar climate feedbacks. Scientists estimate that tens to hundreds of these storms occur globally each year, and that the trend of increasingly severe wildfires will only grow their numbers. Until now, failing to incorporate these storms into Earth system models has hindered our ability to understand this natural disturbance’s impact on global climate.
The research team also included scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, U.C. Irvine, and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. Their breakthrough leveraged the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) to successfully capture the complex interplay between wildfires and the atmosphere.
“Our team developed a novel wildfire–Earth system modeling framework that integrates high-resolution wildfire emissions, a one-dimensional plume-rise model, and fire-induced water vapor transport into DOE’s cutting-edge Earth system model,” Ke said. “This breakthrough advances high-resolution modeling of extreme hazards to improve national resilience and preparedness, and provides the framework for future exploration of these storms at regional and global scales within Earth system models.”
————————————————————————————————————-
More information: The full study, Simulating Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds Using a Multiscale Wildfire Simulation Framework, is available from Geophysical Research Letters at https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2024GL114025
Study authors include: Ziming Ke (DRI/Lawrence Livermore National Lab), Qi Tang (Lawrence Livermore National Lab), Jishi Zhang (Lawrence Livermore National Lab), Yang Chen (UC Irvine), James Randerson (UC Irvine), Jianfeng Li (Pacific NW National Lab), Yunyan Zhang (Lawrence Livermore National Lab)
About DRI
We are Nevada’s non-profit research institute, founded in 1959 to empower experts to focus on science that matters. We work with communities across the state — and the world — to address their most pressing scientific questions. We’re proud that our scientists continuously produce solutions that better human and environmental health.
Scientists at DRI are encouraged to follow their research interests across the traditional boundaries of scientific fields, collaborating across DRI and with scientists worldwide. All faculty support their own research through grants, bringing in nearly $5 to the Nevada economy for every $1 of state funds received. With more than 600 scientists, engineers, students, and staff across our Reno and Las Vegas campuses, we conducted more than $52 million in sponsored research focused on improving peoples’ lives in 2024 alone.
At DRI, science isn’t merely academic — it’s the key to future-proofing our communities and building a better world. For more information, please visit www.dri.edu.
Media Contact
Elyse DeFranco
Lead Science Writer & Public Information Officer
elyse.defranco@www-dev.dri.edu


