Southwest Stormwater Center to Provide Regional Best-Practices Solutions for Stormwater Management, Financing
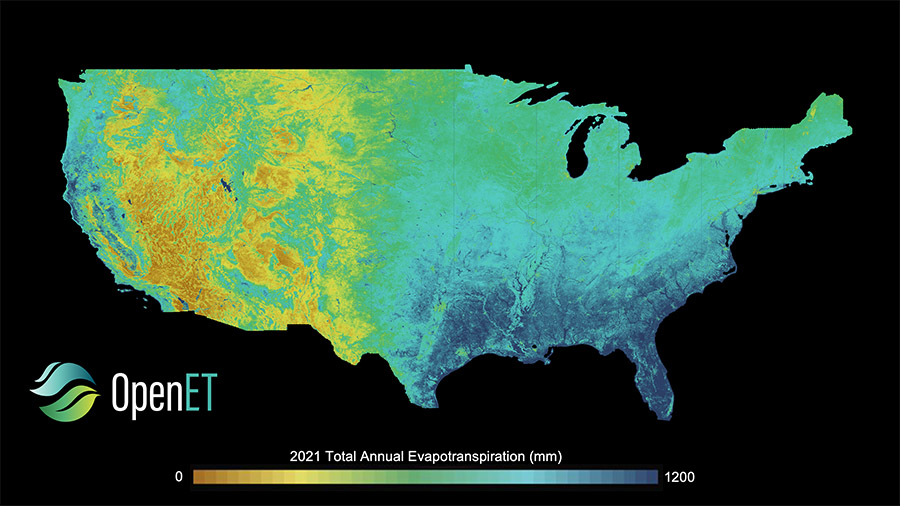
Stormwater management professionals and stakeholders across the U.S. Southwest region will be able to learn about the latest, best-practices solutions for stormwater management and financing through the newly established Southwest Stormwater Center (SWSC), a regional knowledge center for new and emerging stormwater control technologies.